The short version
New preprint! A simple way to extend the classical evidence weighting model of multimodal integration to solve a much wider range of naturalistic tasks. Spoiler: it's nonlinearity. Works for SNNs/ANNs.
Think about the infamous 'cocktail party': you use synchrony between lip movements and sounds to help you hear in a noisy environment. But the classical model throws away that temporal structure, instead just linearly weighting visual and auditory evidence.
We call this algorithm accumulate-then-fuse because first you accumulate evidence over time within a modality, followed by linearly fusing across modalities. We propose instead to (nonlinearly) fuse-then-accumulate. This works much better with pretty much any nonlinearity.
This work started when we were training spiking neural networks with surrogate gradient descent to solve the classical multimodal task where multimodal signals are independent. To our surprise, we didn't need a multimodal area to solve this task! 
In our comodulation tasks the evidence within a modality is forced to be balanced, and only the joint temporal structure carries information. Sure enough, we found you need a multimodal area to do this task (and in unpublished pilot data, the humans in our lab can do this task). 
But this task is kind of unrealistic so we designed a "detection task" where the signal is only on at unknown times, the rest of the time you get noise. You can do this with or without a multimodal area, but there are big differences in performance when the signal is sparse. 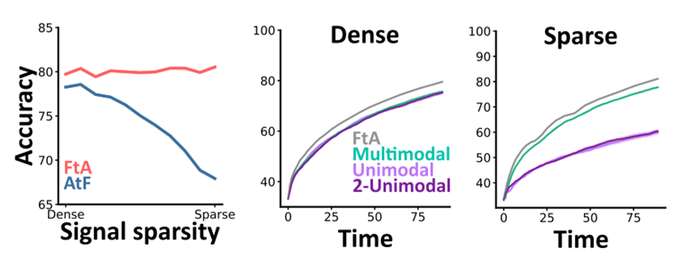
This seems likely to be important in natural settings because fast and accurate reactions to sparse information could make all the difference in a predator-prey interaction. 🐈🐁 And the more complex the task, the bigger the performance difference.
The optimal nonlinearity is softplus(x)=log(1+be^cx) but training artificial neural networks with different nonlinearities like ReLU or sigmoid is just as good in practice. The solution extends to continuous observations, eg. for Gaussian noise you need softplus and quadratic.
Can we relate this to experimental data? One measure used is additivity: how much neurons respond to multimodal signals than you'd guess from unimodal responses. We found high additivity was more important in tasks where FtA did better than AtF, largely due to time constants. 
Plus, we can look at behaviour. In our sparse detection task we can predict which trials subjects are likely to make mistakes on if they use AtF rather than FtA (by plotting trials based on weight of evidence assuming AtF=x or FtA=y). 
We haven't done the experiments to prove this is what we do (yet), but:
⭐ It's consistent with previous experiments (as it is a generalisation of AtF)
⭐ It's the solution found when training spiking or artificial NNs
⭐ It gives better performance with few extra parameters
For more details check out the beautiful HTML version of the preprint on Curvenote (many thanks for the support!) or the good old PDF at bioRxiv.
Nonlinear fusion is optimal for a wide class of multisensory tasks
Abstract
Links
Related videos
-
Multimodal units fuse-then-accumulate evidence across channelsTalk / 2023
Talk on multimodal processing given at VVTNS 2023 seminar series
Related publications
2025
-
Anil S, Goodman DFM, Ghosh M (2025)
Fusing multisensory signals across channels and time.
PLoS Computational Biology
Categories
The short version

Think about the infamous 'cocktail party': you use synchrony between lip movements and sounds to help you hear in a noisy environment. But the classical model throws away that temporal structure, instead just linearly weighting visual and auditory evidence.
We call this algorithm accumulate-then-fuse because first you accumulate evidence over time within a modality, followed by linearly fusing across modalities. We propose instead to (nonlinearly) fuse-then-accumulate. This works much better with pretty much any nonlinearity.
This work started when we were training spiking neural networks with surrogate gradient descent to solve the classical multimodal task where multimodal signals are independent. To our surprise, we didn't need a multimodal area to solve this task! 
In our comodulation tasks the evidence within a modality is forced to be balanced, and only the joint temporal structure carries information. Sure enough, we found you need a multimodal area to do this task (and in unpublished pilot data, the humans in our lab can do this task). 
But this task is kind of unrealistic so we designed a "detection task" where the signal is only on at unknown times, the rest of the time you get noise. You can do this with or without a multimodal area, but there are big differences in performance when the signal is sparse. 
This seems likely to be important in natural settings because fast and accurate reactions to sparse information could make all the difference in a predator-prey interaction. 🐈🐁 And the more complex the task, the bigger the performance difference.
The optimal nonlinearity is softplus(x)=log(1+be^cx) but training artificial neural networks with different nonlinearities like ReLU or sigmoid is just as good in practice. The solution extends to continuous observations, eg. for Gaussian noise you need softplus and quadratic.
Can we relate this to experimental data? One measure used is additivity: how much neurons respond to multimodal signals than you'd guess from unimodal responses. We found high additivity was more important in tasks where FtA did better than AtF, largely due to time constants. 
Plus, we can look at behaviour. In our sparse detection task we can predict which trials subjects are likely to make mistakes on if they use AtF rather than FtA (by plotting trials based on weight of evidence assuming AtF=x or FtA=y). 
We haven't done the experiments to prove this is what we do (yet), but:
⭐ It's consistent with previous experiments (as it is a generalisation of AtF)
⭐ It's the solution found when training spiking or artificial NNs
⭐ It gives better performance with few extra parameters
For more details check out the beautiful HTML version of the preprint on Curvenote (many thanks for the support!) or the good old PDF at bioRxiv.



